Authentication
Insomnia provides a number of authentication helpers to make it trivial to interface with the most common authentication standards. Choose your standard, fill in the prompted fields, and Insomnia will take care of the rest.
Authentication Basics
To set up authentication for a given request, select the desired authentication type from the Auth dropdown. Then, fill out the required fields.
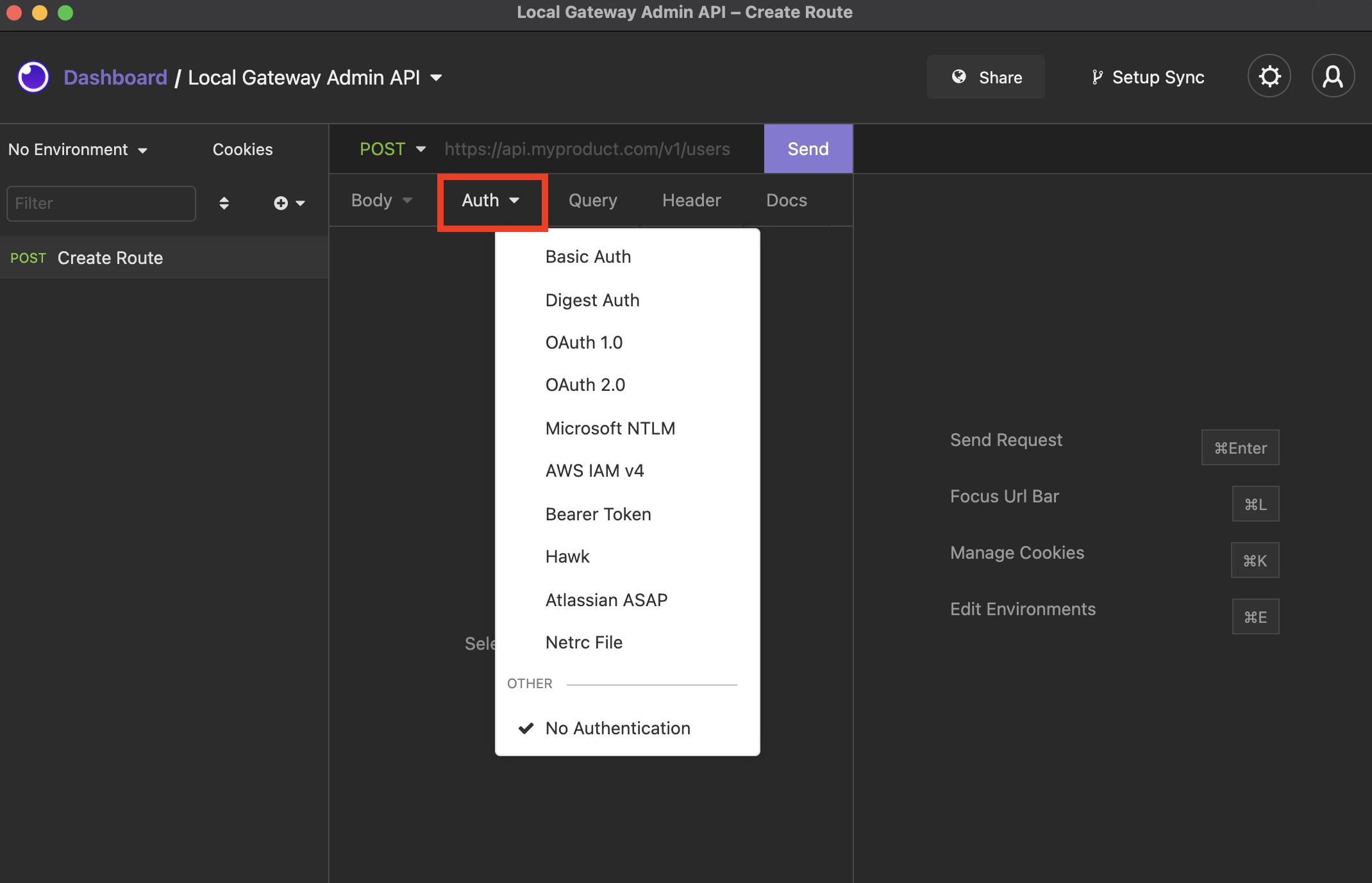 Select your authentication type from the Auth dropdown menu.
Select your authentication type from the Auth dropdown menu.
Supported Authentication Types
Currently, Insomnia supports the following authentication standards.
Basic Auth
Basic authentication is one of the most basic ways to authenticate an HTTP request and is commonly used for passing API keys to authenticate popular APIs such as Stripe.
Digest Auth
Digest is sometimes confused with Basic because it also uses a username and password, but it is much more complicated. To authenticate with a Digest endpoint, the client must send two requests instead of one. The first request sent to the server receives a nonce value, which is then used to produce a one-time-use hash key to authenticate the request.
OAuth 1.0
OAuth 1.0 provides a method for clients to access server resources on behalf of a resource owner. OAuth 1.0 is used for many popular application APIs such as Twitter.
OAuth 2.0
The OAuth 2.0 authorization framework enables applications to obtain limited access to an HTTP service, usually on behalf of a resource owner. OAuth 2.0 is used for many popular application APIs such as GitHub, Facebook, Google, Dropbox, and many more.
Microsoft NTLM
NTLM is the authentication protocol used on networks that include systems running the Windows operating system and on stand-alone systems. Learn more by visiting the Microsoft NTLM Documentation.
AWS IAM v4
AWS IAM v4 is the mechanism used to authenticate with the AWS API. Read more in the AWS Docs Signature Version 4 documentation.
Bearer Token
The bearer token mechanism is commonly used within the OAuth 2.0 protocol and is outlined in RFC6750. When this authentication type is selected, the interface will provide three fields:
-
[Checkbox]ENABLED: Check or un-check this box to send your credentials in theAuthorizationheader. This provides a useful way to keep your credentials in the interface, but not send them. -
TOKEN: The token that will be provided in the
Authorizationheader. -
PREFIX: The prefix for your token. If omitted, the prefix will default to
Bearer. Note that there currently is no way to completely remove the prefix from the header.
The header will be submitted like this:
> Authorization: PREFIX TOKEN
HawK
Hawk is an HTTP authentication scheme using a message authentication code (MAC) algorithm to provide partial HTTP request cryptographic verification. Learn more via the Hawk GitHub project.
Atlassian ASAP
Learn more about Atlassian S2S Authentication Protocol Specification.
Netrc file
The .netrc file contains login and initialization information used by the auto-login process. Learn more via the GNU documentation.
This authentication type requires no user input. The .netrc file on your computer will be located and used automatically.